Background/Terminology
Before we jump into setting up FireSim, it is important to clarify several terms that we will use throughout the rest of this documentation.
First, to disambiguate between the hardware being simulated and the computers doing the simulating, we define:
- Target
The design and environment being simulated. Commonly, a group of one or more RISC-V SoCs with or without a network between them.
- Host
The computers/FPGAs executing the FireSim simulation – the Run Farm below.
We frequently prefix words with these terms. For example, software can run on the simulated RISC-V system (target-software) or on a host x86 machine (host-software).
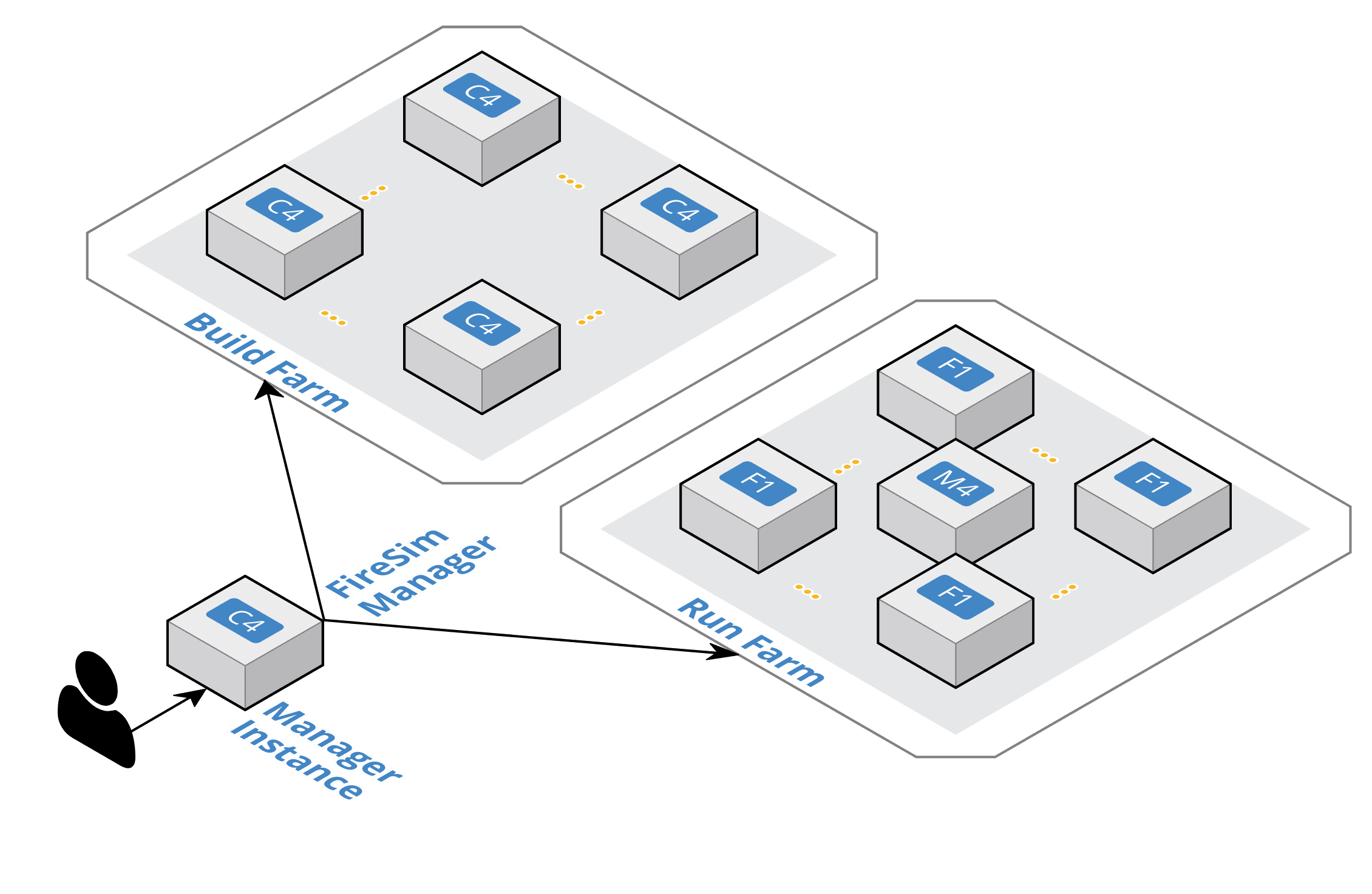
FireSim Infrastructure Diagram
- FireSim Manager (
firesim) This program (available on your path as
firesimonce we source necessary scripts) automates the work required to launch FPGA builds and run simulations. Most users will only have to interact with the manager most of the time. If you’re familiar with tools like Vagrant or Docker, thefiresimcommand is just like thevagrantanddockercommands, but for FPGA simulators instead of VMs/containers.
Machines used to build and run FireSim simulations are broadly classified into three groups:
- Manager Instance
This is the main host machine (e.g., a “vanilla” AWS EC2 instance without an FPGA attached) that you will “do work” on. This is where you’ll clone your copy of FireSim and use the FireSim Manager to deploy builds/simulations from.
- Build Farm Instances
These are a collection of cloud instances (“build farm instances”) that are used by the FireSim manager to run FPGA bitstream builds. The manager will automatically ship all sources necessary to run builds to these instances and will run the Verilog to FPGA bitstream build process on them.
- Run Farm Instances
These are a collection of cloud instances (“run farm instances”) with FPGAs attached that the manager manages and deploys simulations onto. You can use multiple Run Farms in parallel to run multiple separate simulations in parallel.
Later parts of this guide will explain in further detail how each of these instance types is launched and managed.
One final piece of terminology will also be referenced throughout these docs:
- Golden Gate
The FIRRTL compiler in FireSim that converts target RTL into a decoupled simulator. Formerly named MIDAS.